Determination of Eligibility for Special Education and Related Services (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5)
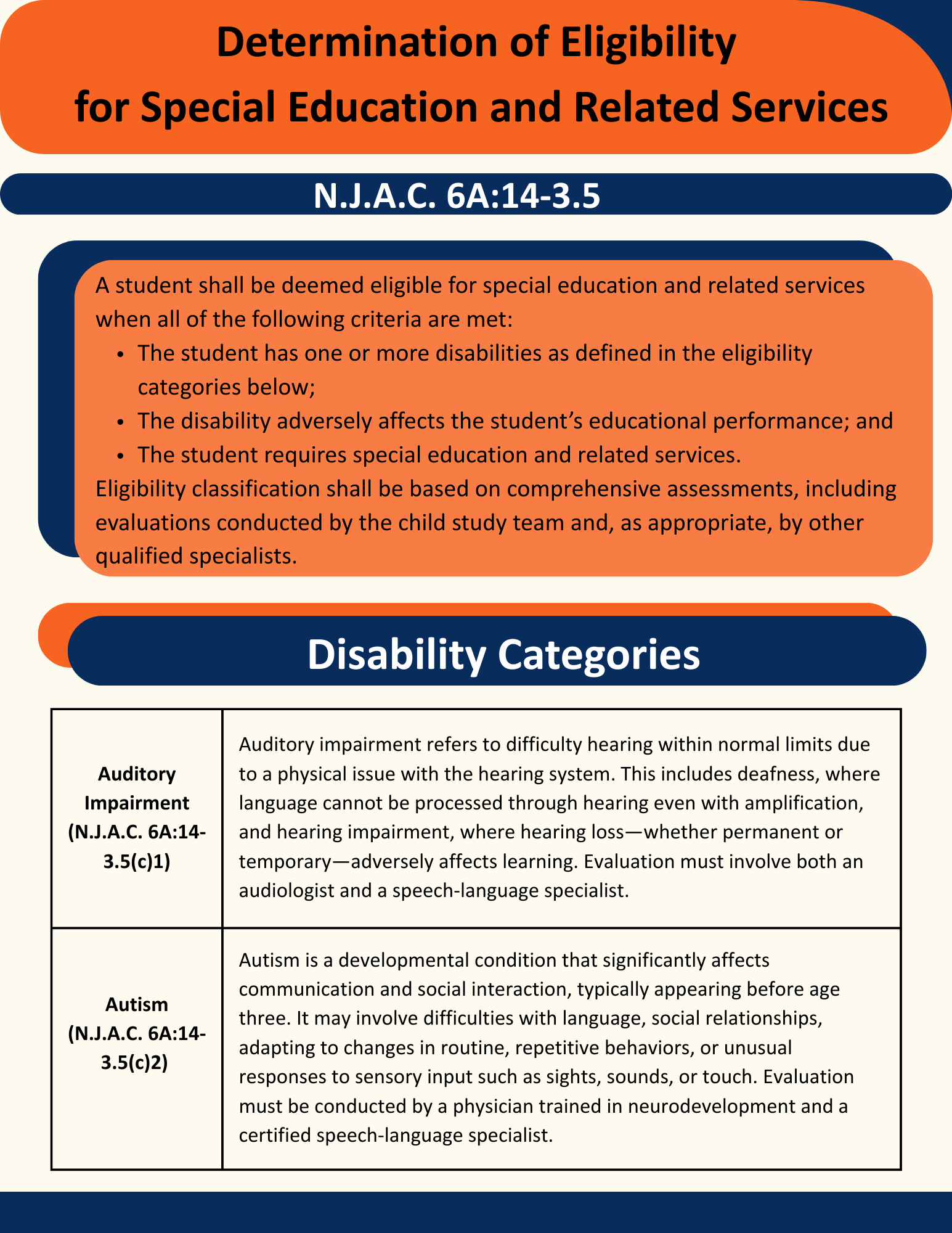
A student shall be deemed eligible for special education and related services when all of the following criteria are met:
- The student has one or more disabilities as defined in the eligibility categories below;
- The disability adversely affects the student’s educational performance; and
- The student requires special education and related services.
Eligibility classification shall be based on comprehensive assessments, including evaluations conducted by the child study team and, as appropriate, by other qualified specialists.
Click here to return to the Parent and Family Engagement Website.
Disability Categories
|
Auditory Impairment (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)1) |
Auditory impairment refers to difficulty hearing within normal limits due to a physical issue with the hearing system. This includes deafness, where language cannot be processed through hearing even with amplification, and hearing impairment, where hearing loss—whether permanent or temporary—adversely affects learning. Evaluation must involve both an audiologist and a speech-language specialist. |
|
Autism (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)2) |
Autism is a developmental condition that significantly affects communication and social interaction, typically appearing before age three. It may involve difficulties with language, social relationships, adapting to changes in routine, repetitive behaviors, or unusual responses to sensory input such as sights, sounds, or touch. Evaluation must be conducted by a physician trained in neurodevelopment and a certified speech-language specialist. |
|
Intellectual Disability (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)3) |
Intellectual disability is characterized by significantly below-average general cognitive functioning that occurs alongside deficits in adaptive behavior. It begins during the developmental period and directly impacts learning and everyday functioning. The disability may be described as mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of support needed in cognitive and adaptive areas. |
|
Communication Impairment (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)4) |
Communication impairment refers to a language disorder that affects the ability to use or understand language and impacts learning. This is not caused by hearing problems. The student must be evaluated through language assessments, including at least one comprehensive test, and the evaluation must be done by a speech-language specialist, who is also considered part of the child study team. |
|
Emotional Regulation Impairment (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)5) |
Emotional regulation impairment is characterized as a long-term emotional or behavioral challenges that affect the ability to learn. This may include difficulties forming relationships, inappropriate behaviors, depression, or physical symptoms related to personal or school problems. These difficulties must not be due to learning or health disabilities. |
|
Multiple Disabilities (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)6) |
Multiple disabilities refer to the presence of two or more disabilities that, together, cause more severe learning needs than either disability alone. Speech-language services alone cannot be one of the disabilities used for this classification. |
|
Deaf-Blindness (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)7 |
Deaf-blindness means combined hearing and vision impairments that together create significant challenges in communication, development, and learning—challenges that are more complex than those caused by each impairment alone. |
|
Orthopedic Impairment (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)8) |
Orthopedic impairment refers to a physical condition that limits the ability to move or control parts of the body and affects educational performance. It can include conditions such as malformation, malfunction, or loss of bones, muscle, or tissue. A medical assessment is required to confirm the condition. |
|
Other Health Impairment (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)9) |
Other Health Impairment is characterized by having a medical condition that limits strength, energy, or alertness, and that affects learning. This includes chronic conditions like ADHD, asthma, diabetes, epilepsy, Tourette Syndrome, or other health issues that impact educational performance. A medical evaluation is required. |
|
Preschool Child with a Disability (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)10) |
Preschool Child with a Disability refers to a child aged 3 to 5 who either exhibits a developmental delay in areas like movement, speech, learning, or social skills, or has a diagnosed disability that impacts the student’s learning. The delay must meet specific criteria in one or more developmental areas. |
|
Specific Learning Disability (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)12) |
Specific learning disability refers a disorder in one or more basic psychological processes involved in understanding or using spoken or written language. It can affect listening, thinking, speaking, reading, writing, spelling, or math skills, including conditions like dyslexia and brain injury. It is identified when a severe discrepancy exists between academic achievement and intellectual ability in areas such as reading, math, oral and written expression, and listening comprehension. Eligibility may also be determined through response to scientifically based interventions as described in N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.4(h)6. |
|
Traumatic Brain Injury (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)13) |
Traumatic brain injury means an acquired injury to the brain caused by an external physical force or insult to the brain, resulting in total or partial functional disability or psychosocial impairment, or both. The term applies to open or closed head injuries resulting in impairments in one or more areas, such as cognition; language; memory; attention; reasoning; abstract thinking; judgment; problem-solving; sensory, perceptual, and motor abilities; psychosocial behavior; physical functions; information processing; and speech. |
|
Visual Impairment (N.J.A.C. 6A:14-3.5(c)14) |
Visual impairment means an impairment in vision that, even with correction, adversely affects a student's educational performance. The term includes both partial sight and blindness. An assessment by a specialist qualified to determine visual disability is required. Students with visual impairments shall be reported to the New Jersey Commission for the Blind and Visually Impaired. |
 Official Site of The State of New Jersey
Official Site of The State of New Jersey